

Lasers are used in a throng of conditions for the retina. Retinal photocoagulation is the mechanism of action for a retinal laser treatment. In this marvel, light energy is converted to heat at the level of the retina, leading to protein denaturation during the retina laser surgery.
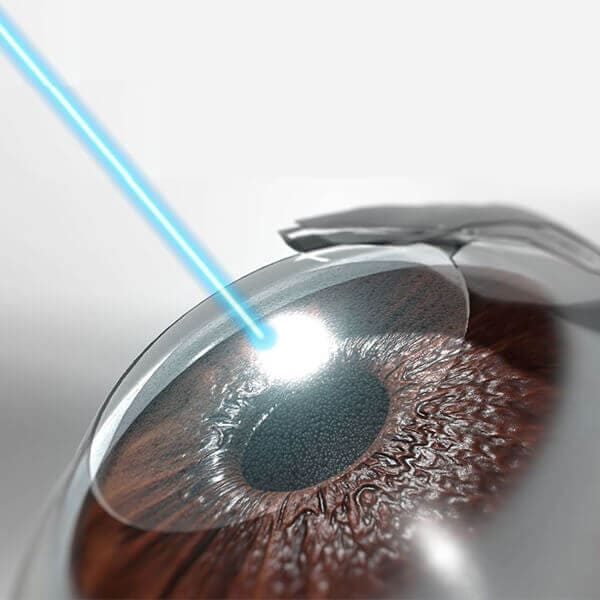
LASIK indicates the correction of low, moderate, and high myopia with and without astigmatism. The specific dioptric limits depend on the particular laser system and the regulatory agency of each country.
Retinal disease is primarily treated using a retina laser. The light energy is absorbed by particular tissue at the back of the eye and transformed to heat with this laser. The heat causes a tiny area of damage to the retina. As the eye heals from this small area of damage, the scar helps to correct the underlying retinal disease. Retina laser is used to seal retinal tears, close leaking blood vessels, or break down abnormal tissue or blood vessels.
