

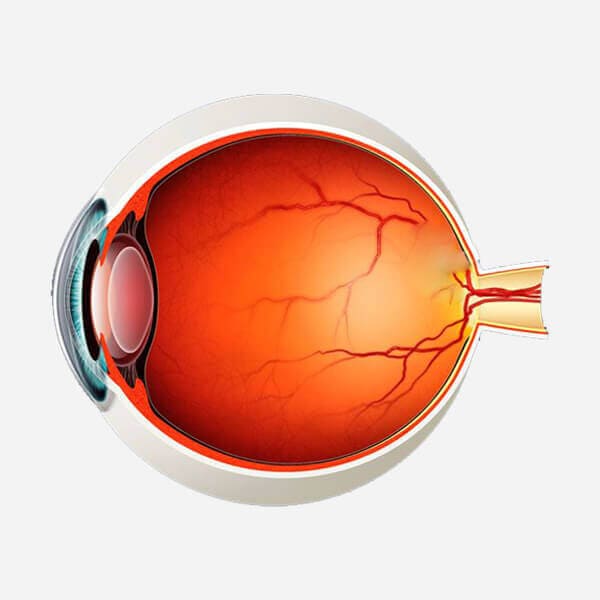
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is an eye disease that affects some premature babies born before 31 weeks of gestation. (A full-term pregnancy lasts between 38 and 42 weeks.) It is a condition that affects the retina, the tissue at the back of the eye. The retina detects light and sends signals to the brain, allowing you to see. Unwanted blood vessels form on the baby's retina as a result of Retinopathy of Prematurity. These blood vessels can lead to serious eye and vision problems in the future.
As an infant grows, ROP may disappear on its own. However, as the infant grows, they should be seen by an ophthalmologist on a regular basis. Sometimes immediate treatment is required to avoid blindness. If not treated promptly, the child may suffer from severe permanent vision loss or even go blind.
An ophthalmologist may initially monitor retinopathy of prematurity to see if it resolves on its own. If the infant's eyes continue to grow abnormal blood vessels, they must be treated.
Retinopathy of Prematurity may be treated by the ophthalmologist in one or more of the following ways:
The ophthalmologist uses a laser to burn away the edge of the retina during laser treatment. The surgeon uses a freezing cold instrument to destroy part of the retina during freezing treatment (cryotherapy). Both of these treatments aim to stop abnormal blood vessel growth in specific areas of the retina.
Anti-VEGF medications are also being used to treat ROP. These medications are injected (as shots) into the eye to prevent abnormal blood vessel growth.
Medication for ROP is also being researched. These medications are injected (as shots) into the eye to prevent abnormal blood vessel growth.
As babies with ROP grow, they must be checked for vision problems by an ophthalmologist on a regular basis. ROP can cause near-sightedness, a detached retina, a lazy eye, or misaligned eyes. It also increases the possibility of developing glaucoma.
VissionTip : Don’t be worried in case you have a premature baby. Get their eyes checked by an Ophthalmologist at the earliest.
